Learning Outcomes
i. Define the phosphodiester bond and its role in nucleic acids.
ii. Understand the process of phosphodiester bond formation through dehydration synthesis.
iii. Recognize the significance of phosphodiester bonds in forming the polymeric structure of nucleic acids.
i. Phosphodiester Bond: The Molecular Bridge of Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids, the molecules that encode genetic information, are composed of long chains of nucleotides. These nucleotides are linked together by a unique type of covalent bond known as the phosphodiester bond. The phosphodiester bond forms a bridge between the sugar molecules of adjacent nucleotides, creating a continuous backbone of alternating sugar-phosphate units.
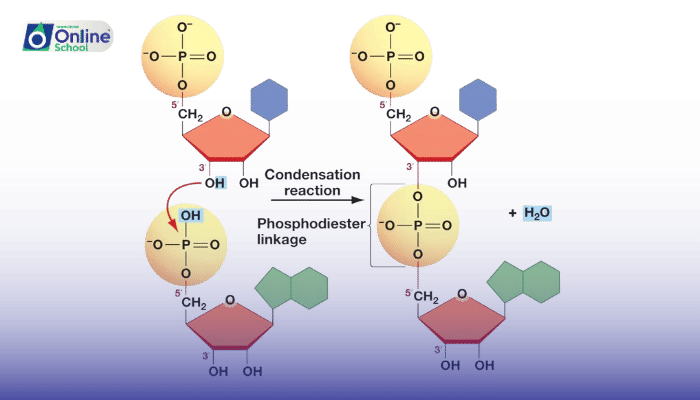
ii. Formation of the Phosphodiester Bond: A Dehydration Synthesis Reaction
The formation of a phosphodiester bond involves a process called dehydration synthesis. During dehydration synthesis, a covalent bond is formed between two molecules with the simultaneous removal of a water molecule. In the case of nucleic acids, the phosphodiester bond is formed between the 3'-carbon atom of the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 5'-carbon atom of the sugar molecule of the adjacent nucleotide.
iii. The Mechanism of Dehydration Synthesis: A Closer Look
The dehydration synthesis reaction involves the following steps:
Nucleophilic Attack: The 3'-phosphate group of one nucleotide acts as a nucleophile, attacking the electrophilic 5'-carbon atom of the sugar molecule of the adjacent nucleotide.
Formation of a Temporary Bond: A temporary covalent bond is formed between the 3'-phosphate group and the 5'-carbon atom.
Elimination of Water: A water molecule is eliminated, leaving behind a stable phosphodiester bond.
iv. The Significance of Phosphodiester Bonds: Building the Nucleic Acid Framework
Phosphodiester bonds play a critical role in the structure and function of nucleic acids. The covalent linkages formed by phosphodiester bonds provide a strong and stable framework for the nucleic acid polymer. This framework allows for the precise arrangement of nucleotides, which is essential for encoding and transmitting genetic information.
v. The Role of Enzymes in Phosphodiester Bond Formation
The formation of phosphodiester bonds is catalyzed by enzymes known as DNA polymerases in DNA and RNA polymerases in RNA. These enzymes facilitate the dehydration synthesis reaction, ensuring the accurate assembly of nucleotides during DNA replication and transcription.
The phosphodiester bond, a covalent linkage between nucleotides, is the molecular signature of nucleic acids. This bond forms the backbone of nucleic acid polymers, providing structural support and allowing for the precise arrangement of nucleotides, which is crucial for encoding and transmitting genetic information. The formation of phosphodiester bonds is mediated by enzymes, highlighting the intricate interplay between molecular structure and biological function.